Electric Vehicle Basics
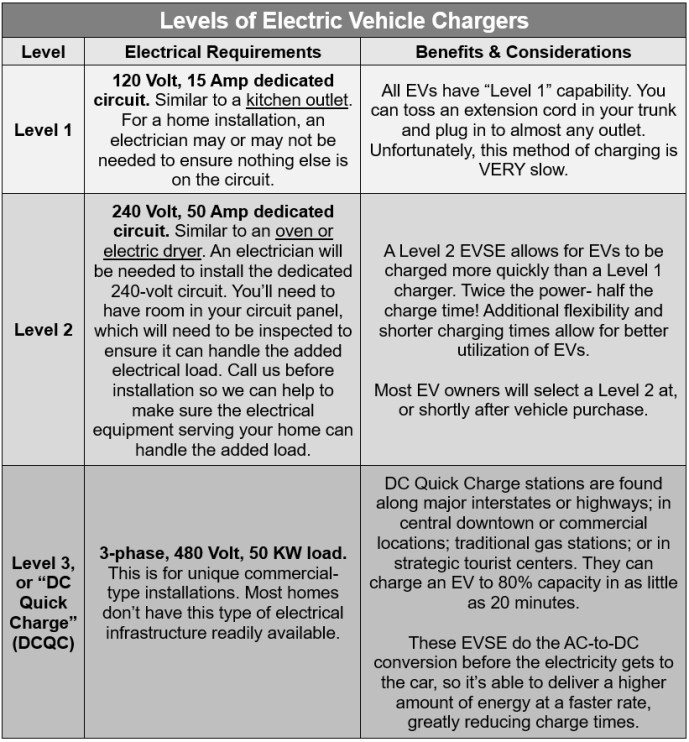
Electric Vehicles (EVs) run on energy stored in batteries. Batteries store energy as DC (direct current), but our power grid uses AC (alternating current). EVs have an on-board inverter to change the type of electricity from supplied AC to needed DC. You can plug any EV into a dedicated 120 volt, 15 amp circuit and get it to charge, but it’s going to take a while.
This is where EV chargers, or Electric Vehicle Service Equipment (EVSE) comes in handy. EVSE comes in 3 basic “levels”. For quick reference, a level 1 charger is equivalent to plugging in a hairdryer, level 2 is similar to running your oven or dryer, and level 3 is like powering multiple homes.
Learn more from these great EV Charging Guides:
For People: PlugShare
For Businesses: PlugShare for Business
Are you looking to install an EV Charger?
Residential Customers: We recommend contacting a licensed electrician to start the process. If it is determined that your service is unable to support the additional load, please contact us to request a service upgrade. To learn more, please visit: Upgrade Service.
Commercial Customers: Depending on your circumstances, you'll either need to follow the Line Extension Application process or the service upgrade process to get started.
***Please reach out to your local city or county planning department regarding permit requirements and questions.***
